Best Practices of Data Management
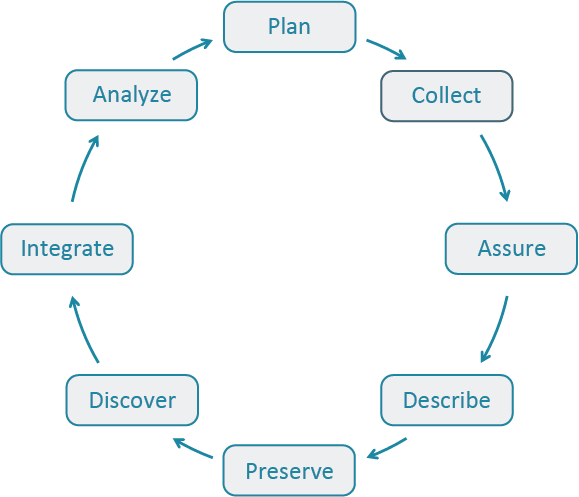
The Skillbuilding Hub Best Practices database provides individuals with recommendations on how to effectively work with their data through all stages of the data lifecycle. Users can access best practices within the database by clicking on a stage of the lifecycle or scrolling down.
Best Practices Primer
For students and others new to data management, DataONE provides a Best Practices Primer as an introduction to this Best Practices database and data management in general.
Public Participation in Science Research Data Management
DataONE also provides a Data Management Guide written specifically for the Citizen Science community that takes the users through the steps of the data lifecycle and links to various Best Practices online.
Best Practice by Data Life Cycle stage
Analyze
- Describe method to create derived data products
When describing the process for creating derived data products, the following information should be included in the data documentation or the companion metadata file: - Document steps used in data processing
Different types of new data may be created in the course of a project, for instance visualizations, plots, statistical outputs, a new dataset created by integrating multiple datasets, etc. Whenever possible, document your workflow (the process used to c...analyze data processing describe integrate provenance replicable data
- Ensure datasets used are reproducible
When searching for data, whether locally on one’s machine or in external repositories, one may use a variety of search terms. In addition, data are often housed in databases or clearinghouses where a query is required in order access data. In order to r...analyze assure data archives data processing discover provenance replicable data
- Identify most appropriate software
Follow the steps below to choose the most appropriate software to meet your needs. Identify what you want to achieve (discover data, analyze data, write a paper, etc.) Identify the necessary software features for your project (i.e. functional requi... - Identify outliers
Outliers may not be the result of actual observations, but rather the result of errors in data collection, data recording, or other parts of the data life cycle. The following can be used to identify outliers for closer examination: - Identify values that are estimated
Data tables should ideally include values that were acquired in a consistent fashion. However, sometimes instruments fail and gaps appear in the records. For example, a data table representing a series of temperature measurements collected over time fro... - Store data with appropriate precision
Data should not be entered with higher precision than they were collected in (e.g if a device collects data to 2dp, an Excel file should not present it to 5 dp). If the system stores data in higher precision, care needs to be taken when exporting to ASC... - Understand the geospatial parameters of multiple data sources
Understand the input geospatial data parameters, including scale, map projection, geographic datum, and resolution, when integrating data from multiple sources. Care should be taken to ensure that the geospatial parameters of the source datasets can be ...analyze documentation geography geospatial integrate metadata provenance
Assure
- Communicate data quality
Information about quality control and quality assurance are important components of the metadata: - Confirm a match between data and their description in metadata
To assure that metadata correctly describes what is actually in a data file, visual inspection or analysis should be done by someone not otherwise familiar with the data and its format. This will assure that the metadata is sufficient to describe the da...assure data consistency describe documentation metadata quality
- Consider the compatibility of the data you are integrating
The integration of multiple data sets from different sources requires that they be compatible. Methods used to create the data should be considered early in the process, to avoid problems later during attempts to integrate data sets. Note that just beca... - Develop a quality assurance and quality control plan
Just as data checking and review are important components of data management, so is the step of documenting how these tasks were accomplished. Creating a plan for how to review the data before it is collected or compiled allows a researcher to think sys... - Double-check the data you enter
Ensuring accuracy of your data is critical to any analysis that follows. - Ensure basic quality control
Quality control practices are specific to the type of data being collected, but some generalities exist: - Ensure datasets used are reproducible
When searching for data, whether locally on one’s machine or in external repositories, one may use a variety of search terms. In addition, data are often housed in databases or clearinghouses where a query is required in order access data. In order to r...analyze assure data archives data processing discover provenance replicable data
- Identify missing values and define missing value codes
Missing values should be handled carefully to avoid their affecting analyses. The content and structure of data tables are best maintained when consistent codes are used to indicate that a value is missing in a data field. Commonly used approaches for c... - Identify outliers
Outliers may not be the result of actual observations, but rather the result of errors in data collection, data recording, or other parts of the data life cycle. The following can be used to identify outliers for closer examination: - Identify values that are estimated
Data tables should ideally include values that were acquired in a consistent fashion. However, sometimes instruments fail and gaps appear in the records. For example, a data table representing a series of temperature measurements collected over time fro... - Mark data with quality control flags
As part of any review or quality assurance of data, potential problems can be categorized systematically. For example data can be labeled as 0 for unexamined, -1 for potential problems and 1 for “good data.” Some research communities have developed stan... - Provide version information for use and discovery
Provide versions of data products with defined identifiers to enable discovery and use.
Collect
- Preserve information: Keep raw data raw
In order to preserve the raw data for future use: - Use appropriate field delimiters
Delimit the columns within a data table using commas or tabs; these are listed in order of preference. Semicolons are used in many systems as line end delimiters and may cause problems if data are imported into those systems (e.g. SAS, PHP scripts). Avo... - Use consistent codes
Be consistent in the use of codes to indicate categorical variables, for example species names, sites, or land cover types. Codes should always be the same within one data set. Pay particular attention to spelling and case; most frequent problems are wi...
Describe
- Assign descriptive file names
File names should reflect the contents of the file and include enough information to uniquely identify the data file. File names may contain information such as project acronym, study title, location, investigator, year(s) of study, data type, version n... - Choose and use standard terminology to enable discovery
Terms and phrases that are used to represent categorical data values or for creating content in metadata records should reflect appropriate and accepted vocabularies in your community or institution. Methods used to identify and select the proper termin...controlled vocabulary describe documentation metadata ontologies preserve standards
- Confirm a match between data and their description in metadata
To assure that metadata correctly describes what is actually in a data file, visual inspection or analysis should be done by someone not otherwise familiar with the data and its format. This will assure that the metadata is sufficient to describe the da...assure data consistency describe documentation metadata quality
- Create a data dictionary
A data dictionary provides a detailed description for each element or variable in your dataset and data model. Data dictionaries are used to document important and useful information such as a descriptive name, the data type, allowed values, units, and ...controlled vocabulary describe documentation metadata terminology units
- Define the data model
A data model documents and organizes data, how it is stored and accessed, and the relationships among different types of data. The model may be abstract or concrete. - Define the parameters
The parameters reported in the data set need to have names that clearly describe the contents. Ideally, the names should be standardized across files, data sets, and projects, in order that others can readily use the information. - Describe format for spatial location
Spatial coordinates should be reported in decimal degrees format to at least 4 (preferably 5 or 6) significant digits past the decimal point. An accuracy of 1.11 meters at the equator is represented by +/- 0.00001. This does not include uncertainty intr... - Describe formats for date and time
For date, always include four digit year and use numbers for months. For example, the date format yyyy-mm-dd would appear as 2011-03-15 (March 15, 2011). - Describe measurement techniques
Data measurement descriptions should: - Describe method to create derived data products
When describing the process for creating derived data products, the following information should be included in the data documentation or the companion metadata file: - Describe the contents of data files
A description of the contents of the data file should contain the following: - Describe the overall organization of your dataset
Data sets or collections are often composed of multiple files that are related. Files may have come from (or still be stored in) a relational database, and the relationships among the data tables or other entities are important if the data are to be reu... - Describe the research project
The research project description should contain the following information:annotation data creators describe geography geospatial measurement
- Describe the sensor network
If your project uses a sensor network, you should describe and document that network and the instruments it uses. This information is essential to understanding and interpreting the data you use, and should be included as a part of the metadata generate... - Describe the spatial extent and resolution of your dataset
The spatial extent of your data set or collection as a whole should be described. The minimum acceptable description would be a bounding box describing the northern most, southern most, western most, and eastern most limits of the data.describe documentation geospatial location measurement metadata
- Describe the temporal extent and resolution of your dataset
The temporal extent over which the data within your dataset or collection was acquired or collected should be described. Normally this is done by providing - Describe the units of measurement for each observation
The units of reported parameters need to be explicitly stated in the data file and in the documentation. We recommend SI units (The International System of Units) but recognize that each discipline has its own commonly used units of measure. The critica... - Document and store data using stable file formats
File formats are important for understanding how data can be used and possibly integrated. The following issues need to be documented: Does the file format of the data adhere to one or more standards? Is that file standard an open (i.e. open source... - Document steps used in data processing
Different types of new data may be created in the course of a project, for instance visualizations, plots, statistical outputs, a new dataset created by integrating multiple datasets, etc. Whenever possible, document your workflow (the process used to c...analyze data processing describe integrate provenance replicable data
- Describe the overall organization of your dataset
Identification of any species represented in the data set should be as complete as possible. - Document your data organization strategy
The following are strategies for effective data organization: Sparse matrix: Optimal data models for storing data avoid sparse matrices, i.e. if many data points within a matrix are empty a data table with a column for parameters and a column for val...data management plan data model data normalization database describe
- Ensure flexible data services for virtual datasets
In order for a large dataset to be effectively used by a variety of end users, the following procedures for preparing a virtual dataset are recommended: - Identify and use relevant metadata standards
Many times significant overlap exists among metadata content standards. You should identify those standards that include the fields needed to describe your data. In order to describe your data, you need to decide what information is required for data us...controlled vocabulary describe documentation format metadata preserve
- Maintain consistent data typing
Choose the right data type and precision for data in each column. As examples: (1) use date fields for dates; and (2) use numerical fields with decimal places precision. Comments and explanations should not be included in a column that is meant to inclu... - Provide a citation and document provenance for your dataset
For appropriate attribution and provenance of a dataset, the following information should be included in the data documentation or the companion metadata file:citation data creators data source describe preserve provenance
- Provide capabilities for tagging and annotation of your data by the community
People have different perspectives on what data means to them, and how it can be used and interpreted in different contexts. Data users ranging from community participants to researchers in different domains can provide unique and valuable insights into...annotation controlled vocabulary describe documentation metadata
- Provide identifier for dataset used
In order to ensure replicable data access:access data consistency describe preserve provenance replicable data
- Separate data values from annotations
A separate column should be used for data qualifiers, descriptions, and flags, otherwise there is the potential for problems to develop during analyses. Potential entries in the descriptor column: - Sharing data: legal and policy considerations
All research requires the sharing of information and data. The general philosophy is that data are freely and openly shared. However, funding organizations and institutions may require that their investigators cite the impact of their work, including sh... - Use appropriate field delimiters
Delimit the columns within a data table using commas or tabs; these are listed in order of preference. Semicolons are used in many systems as line end delimiters and may cause problems if data are imported into those systems (e.g. SAS, PHP scripts). Avo... - Use consistent codes
Be consistent in the use of codes to indicate categorical variables, for example species names, sites, or land cover types. Codes should always be the same within one data set. Pay particular attention to spelling and case; most frequent problems are wi...
Discover
- Advertise your data using datacasting tools
To make your data available using standard and open software tools you should: - Assign descriptive file names
File names should reflect the contents of the file and include enough information to uniquely identify the data file. File names may contain information such as project acronym, study title, location, investigator, year(s) of study, data type, version n... - Check data and other outputs for print and web accessibility
To maximize usability of your data or outputs, ensure that those with impairments or disabilities will still be able to access and understand them. The Web Accessibility Initiative, from the W3C, suggests that those producing content for others consider... - Ensure datasets used are reproducible
When searching for data, whether locally on one’s machine or in external repositories, one may use a variety of search terms. In addition, data are often housed in databases or clearinghouses where a query is required in order access data. In order to r...analyze assure data archives data processing discover provenance replicable data
Integrate
- Document steps used in data processing
Different types of new data may be created in the course of a project, for instance visualizations, plots, statistical outputs, a new dataset created by integrating multiple datasets, etc. Whenever possible, document your workflow (the process used to c...analyze data processing describe integrate provenance replicable data
- Document the integration of multiple datasets
Document the steps used to integrate disparate datasets. Ideally, one would adopt mechanisms to systematically capture the integration process, e.g. in an executable form such as a script or workflow, so that it can be reproduced In lieu of a scien...citation data consistency documentation integrate metadata provenance
- Provide budget information for your data management plan
As a best practice, one must first acknowledge that the process of managing data will incur costs. Researchers should plan to address these costs and the allocation of resources in the early planning phases of the project. This best practice focuses on ... - Understand the geospatial parameters of multiple data sources
Understand the input geospatial data parameters, including scale, map projection, geographic datum, and resolution, when integrating data from multiple sources. Care should be taken to ensure that the geospatial parameters of the source datasets can be ...analyze documentation geography geospatial integrate metadata provenance
Life cycle stage here
- How to write a Best Practice file
Filename
Plan
- Create and document a data backup policy
A backup policy helps manage users’ expectations and provides specific guidance on the “who, what, when, and how” of the data backup and restore process. There are several benefits to documenting your data backup policy: Helps clarify the policies, p... - Create, manage, and document your data storage system
Data files should be managed to avoid disorder. To facilitate access to files, all storage devices, locations and access accounts should be documented and accessible to team members. Use appropriate tools, such as version control tools, to keep track of... - Define expected data outcomes and types
In the planning process, researchers should carefully consider what data will be produced in the course of their project. - Define roles and assign responsibilities for data management
In addition to the primary researcher(s), there might be others involved in the research process that take part in aspects of data management. By clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of the parties involved, data are more likely to be availab... - Define the data model
A data model documents and organizes data, how it is stored and accessed, and the relationships among different types of data. The model may be abstract or concrete. - Identify data sensitivity
Steps for the identification of the sensitivity of data and the determination of the appropriate security or privacy level are: Determine if the data has any confidentiality concerns Can an unauthorized individual use the information to do... - Identify suitable repositories for the data
Shaping the data management plan towards a specific desired repository will increase the likelihood that the data will be accepted into that repository and increase the discoverability of the data within the desired repository. When beginning a data man... - Plan data management early in your project
A Data Management Plan should include the following information: - Plan for effective multimedia management
Multimedia data present unique challenges for data discovery, accessibility, and metadata formatting and should be thoughtfully managed. Researchers should establish their own requirements for management of multimedia during and after a research project... - Provide budget information for your data management plan
As a best practice, one must first acknowledge that the process of managing data will incur costs. Researchers should plan to address these costs and the allocation of resources in the early planning phases of the project. This best practice focuses on ... - Revisit data management plan throughout the project life cycle
The plan will be created at the conceptual stage of the project. It should be considered a living document and a road map for the project, and should be closely followed. Any changes to the data management plan should be made deliberately, and the plan ...
Preserve
- Backup your data
To avoid accidental loss of data you should: - Choose and use standard terminology to enable discovery
Terms and phrases that are used to represent categorical data values or for creating content in metadata records should reflect appropriate and accepted vocabularies in your community or institution. Methods used to identify and select the proper termin...controlled vocabulary describe documentation metadata ontologies preserve standards
- Create and document a data backup policy
A backup policy helps manage users’ expectations and provides specific guidance on the “who, what, when, and how” of the data backup and restore process. There are several benefits to documenting your data backup policy: Helps clarify the policies, p... - Decide what data to preserve
The process of science generates a variety of products that are worthy of preservation. Researchers should consider all elements of the scientific process in deciding what to preserve: - Ensure flexible data services for virtual datasets
In order for a large dataset to be effectively used by a variety of end users, the following procedures for preparing a virtual dataset are recommended: - Ensure integrity and accessibility when making backups of data
For successful data replication and backup: - Ensure the reliability of your storage media
All storage media, whether hard drives, discs or data tapes, will wear out over time, rendering your data files inaccessible. To ensure ongoing access to both your active data files and your data archives, it is important to continually monitor the cond...access backup data archives disaster recovery preserve restore storage
- Identify and use relevant metadata standards
Many times significant overlap exists among metadata content standards. You should identify those standards that include the fields needed to describe your data. In order to describe your data, you need to decide what information is required for data us...controlled vocabulary describe documentation format metadata preserve
- Identify data sensitivity
Steps for the identification of the sensitivity of data and the determination of the appropriate security or privacy level are: Determine if the data has any confidentiality concerns Can an unauthorized individual use the information to do... - Identify data with long-term value
As part of the data life cycle, research data will be contributed to a repository to support preservation and discovery. A research project may generate many different iterations of the same dataset - for example, the raw data from the instruments, as w... - Identify suitable repositories for the data
Shaping the data management plan towards a specific desired repository will increase the likelihood that the data will be accepted into that repository and increase the discoverability of the data within the desired repository. When beginning a data man... - Plan data management early in your project
A Data Management Plan should include the following information: - Plan for effective multimedia management
Multimedia data present unique challenges for data discovery, accessibility, and metadata formatting and should be thoughtfully managed. Researchers should establish their own requirements for management of multimedia during and after a research project... - Preserve information: Keep raw data raw
In order to preserve the raw data for future use: - Provide a citation and document provenance for your dataset
For appropriate attribution and provenance of a dataset, the following information should be included in the data documentation or the companion metadata file:citation data creators data source describe preserve provenance
- Provide identifier for dataset used
In order to ensure replicable data access:access data consistency describe preserve provenance replicable data
- Provide version information for use and discovery
Provide versions of data products with defined identifiers to enable discovery and use. - Recognize stakeholders in data ownership
When creating the data management plan, review all who may have a stake in the data so future users of the data can easily track who may need to give permission. Possible stakeholders include but are not limited to: - Store data with appropriate precision
Data should not be entered with higher precision than they were collected in (e.g if a device collects data to 2dp, an Excel file should not present it to 5 dp). If the system stores data in higher precision, care needs to be taken when exporting to ASC...

